metan v1.8.1 now on CRAN
I’m so excited to announce that the latest stable version (v1.8.1) of the R package metan is now on
CRAN. The main features included in this version are detailed below.
- New function
gytb()to generate the Genotype by yield*trait biplot analysis.
library(metan)
# Registered S3 method overwritten by 'GGally':
# method from
# +.gg ggplot2
# |========================================================|
# | Multi-Environment Trial Analysis (metan) v1.13.0 |
# | Author: Tiago Olivoto |
# | Type 'citation('metan')' to know how to cite metan |
# | Type 'vignette('metan_start')' for a short tutorial |
# | Visit 'https://bit.ly/2TIq6JE' for a complete tutorial |
# |========================================================|
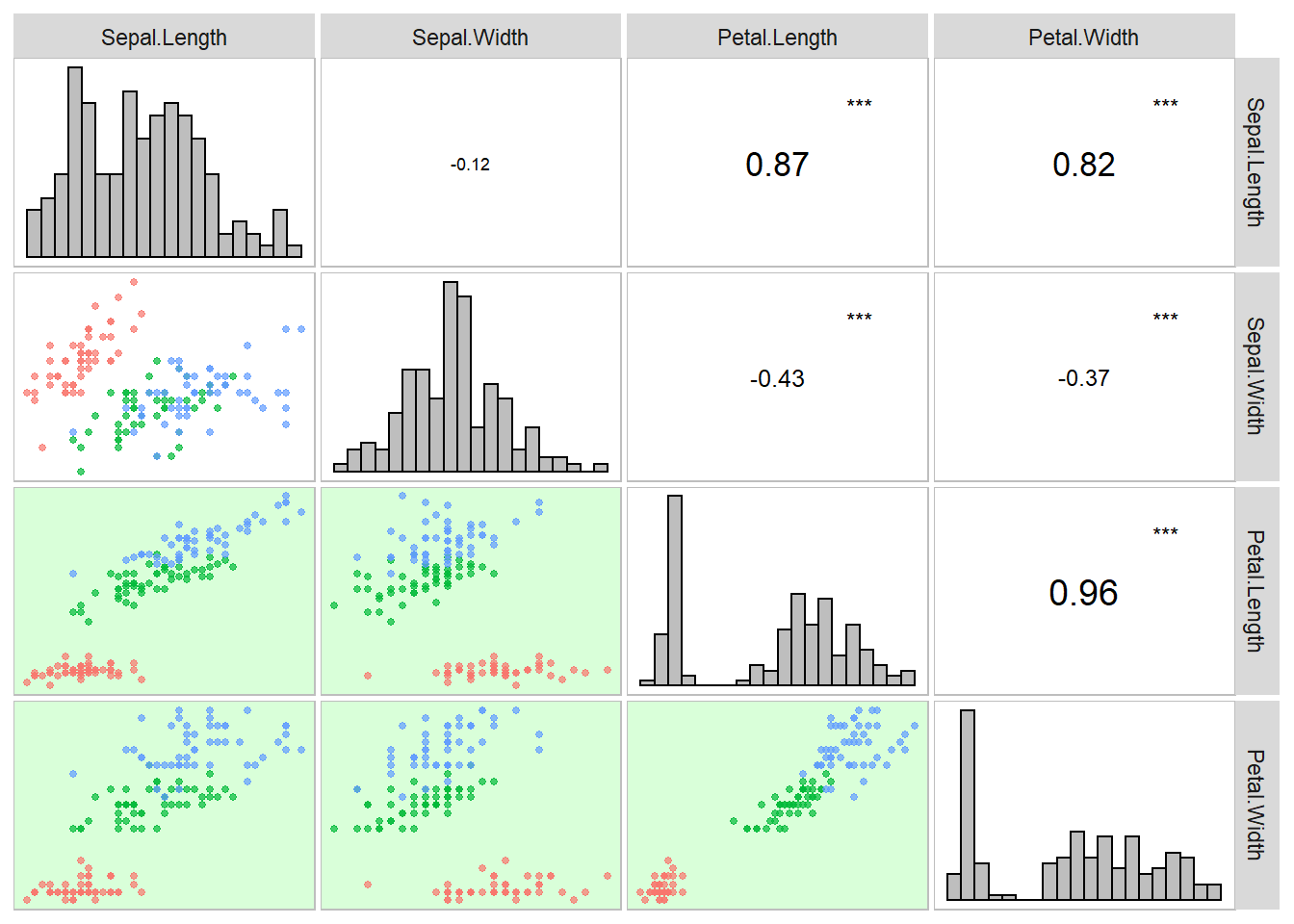
mod <- gytb(data_ge2,
gen = GEN,
yield = EL)
plot(mod)
# Warning: ggrepel: 1 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider
# increasing max.overlaps
- New functions
row_col_mean()androw_col_sum()to add a row with the mean/sum of each variable and a column with the the mean/sum for each row of a matrix or data frame.
mat <- make_mat(data_ge, ENV, GEN, GY) %>% round_cols()
mat
# G1 G10 G2 G3 G4 G5 G6 G7 G8 G9
# E1 2.37 1.97 2.90 2.89 2.59 2.19 2.30 2.77 2.90 2.33
# E10 2.31 1.54 2.30 2.34 2.17 2.14 2.21 2.44 2.57 1.74
# E11 1.36 0.90 1.49 1.57 1.37 1.33 1.50 1.36 1.68 1.13
# E12 1.34 1.02 1.99 1.76 1.53 1.69 1.39 1.95 2.00 1.41
# E13 3.00 1.83 3.03 3.47 2.64 2.57 2.91 3.18 3.52 2.95
# E14 1.53 1.86 1.43 2.06 1.86 1.78 1.80 1.94 1.99 1.57
# E2 3.04 3.15 3.23 3.61 3.19 3.14 3.29 2.61 3.44 3.09
# E3 4.08 4.11 4.57 4.13 3.85 3.74 3.43 4.10 4.11 4.51
# E4 3.49 4.27 3.72 4.13 3.30 3.38 3.40 3.02 4.14 3.90
# E5 4.17 3.37 3.83 4.13 3.78 3.47 3.57 4.05 4.81 3.93
# E6 2.81 2.48 2.54 2.98 2.70 2.43 2.34 2.67 2.91 2.77
# E7 1.90 2.24 1.99 2.16 1.98 1.66 1.76 2.55 2.26 1.39
# E8 2.27 2.70 2.05 2.85 2.30 2.71 2.54 2.58 2.88 2.49
# E9 2.78 3.15 3.36 3.29 3.72 3.30 3.04 3.14 2.83 1.94
row_col_mean(mat) %>% round_cols()
# G1 G10 G2 G3 G4 G5 G6 G7 G8 G9 row_means
# E1 2.37 1.97 2.90 2.89 2.59 2.19 2.30 2.77 2.90 2.33 2.52
# E10 2.31 1.54 2.30 2.34 2.17 2.14 2.21 2.44 2.57 1.74 2.18
# E11 1.36 0.90 1.49 1.57 1.37 1.33 1.50 1.36 1.68 1.13 1.37
# E12 1.34 1.02 1.99 1.76 1.53 1.69 1.39 1.95 2.00 1.41 1.61
# E13 3.00 1.83 3.03 3.47 2.64 2.57 2.91 3.18 3.52 2.95 2.91
# E14 1.53 1.86 1.43 2.06 1.86 1.78 1.80 1.94 1.99 1.57 1.78
# E2 3.04 3.15 3.23 3.61 3.19 3.14 3.29 2.61 3.44 3.09 3.18
# E3 4.08 4.11 4.57 4.13 3.85 3.74 3.43 4.10 4.11 4.51 4.06
# E4 3.49 4.27 3.72 4.13 3.30 3.38 3.40 3.02 4.14 3.90 3.67
# E5 4.17 3.37 3.83 4.13 3.78 3.47 3.57 4.05 4.81 3.93 3.91
# E6 2.81 2.48 2.54 2.98 2.70 2.43 2.34 2.67 2.91 2.77 2.66
# E7 1.90 2.24 1.99 2.16 1.98 1.66 1.76 2.55 2.26 1.39 1.99
# E8 2.27 2.70 2.05 2.85 2.30 2.71 2.54 2.58 2.88 2.49 2.54
# E9 2.78 3.15 3.36 3.29 3.72 3.30 3.04 3.14 2.83 1.94 3.06
# col_means 2.60 2.47 2.74 2.96 2.64 2.54 2.53 2.74 3.00 2.51 2.67
row_col_sum(mat) %>% round_cols()
# G1 G10 G2 G3 G4 G5 G6 G7 G8 G9 row_sums
# E1 2.37 1.97 2.90 2.89 2.59 2.19 2.30 2.77 2.90 2.33 25.21
# E10 2.31 1.54 2.30 2.34 2.17 2.14 2.21 2.44 2.57 1.74 21.76
# E11 1.36 0.90 1.49 1.57 1.37 1.33 1.50 1.36 1.68 1.13 13.69
# E12 1.34 1.02 1.99 1.76 1.53 1.69 1.39 1.95 2.00 1.41 16.08
# E13 3.00 1.83 3.03 3.47 2.64 2.57 2.91 3.18 3.52 2.95 29.10
# E14 1.53 1.86 1.43 2.06 1.86 1.78 1.80 1.94 1.99 1.57 17.82
# E2 3.04 3.15 3.23 3.61 3.19 3.14 3.29 2.61 3.44 3.09 31.79
# E3 4.08 4.11 4.57 4.13 3.85 3.74 3.43 4.10 4.11 4.51 40.63
# E4 3.49 4.27 3.72 4.13 3.30 3.38 3.40 3.02 4.14 3.90 36.75
# E5 4.17 3.37 3.83 4.13 3.78 3.47 3.57 4.05 4.81 3.93 39.11
# E6 2.81 2.48 2.54 2.98 2.70 2.43 2.34 2.67 2.91 2.77 26.63
# E7 1.90 2.24 1.99 2.16 1.98 1.66 1.76 2.55 2.26 1.39 19.89
# E8 2.27 2.70 2.05 2.85 2.30 2.71 2.54 2.58 2.88 2.49 25.37
# E9 2.78 3.15 3.36 3.29 3.72 3.30 3.04 3.14 2.83 1.94 30.55
# col_sums 36.45 34.59 38.43 41.37 36.98 35.53 35.48 38.36 42.04 35.15 374.38
inspect()now generate a warning if zero values are observed in data.
data_zero <- data_ge
data_zero[3, 4] <- 0
inspect(data_ge)
# # A tibble: 5 x 9
# Variable Class Missing Levels Valid_n Min Median Max Outlier
# <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
# 1 ENV factor No 14 420 NA NA NA NA
# 2 GEN factor No 10 420 NA NA NA NA
# 3 REP factor No 3 420 NA NA NA NA
# 4 GY numeric No - 420 0.67 2.61 5.09 0
# 5 HM numeric No - 420 38 48 58 0
# No issues detected while inspecting data.
inspect(data_zero)
# # A tibble: 5 x 9
# Variable Class Missing Levels Valid_n Min Median Max Outlier
# <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
# 1 ENV factor No 14 420 NA NA NA NA
# 2 GEN factor No 10 420 NA NA NA NA
# 3 REP factor No 3 420 NA NA NA NA
# 4 GY numeric No - 420 0 2.61 5.09 0
# 5 HM numeric No - 420 38 48 58 0
# Warning: Zero values observed in variable(s) GY.
- New functions
has_zero(),remove_cols_zero(),remove_rows_zero(),select_cols_zero(),select_rows_zero(), andreplace_zero()to deal with 0s in a data frame.
data_naz <- data_g %>% round_cols(digits = 1)
data_naz[c(2, 6, 9), c(6:7, 12:13)] <- 0
has_zero(data_naz)
# [1] TRUE
remove_cols_zero(data_naz)
# Warning: Column(s) EL, ED, NR, NKR with 0s deleted.
# # A tibble: 39 x 13
# GEN REP PH EH EP CL CD CW KW CDED PERK TKW NKE
# <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
# 1 H1 1 2.1 1 0.5 30.5 16.6 28.6 164. 0.6 85.1 347. 458.
# 2 H1 2 2.2 1.1 0.5 30.5 14.7 22.3 130. 0.6 85.2 337. 386.
# 3 H1 3 2.3 1.2 0.5 31.7 16.2 29.6 176 0.6 85.9 422. 431.
# 4 H10 1 1.8 0.9 0.5 26.2 15 12.9 116. 0.6 89.8 258. 446.
# 5 H10 2 2.1 1 0.5 23.5 14.4 11.5 118. 0.5 91.1 233. 496.
# 6 H10 3 2.3 1.1 0.5 24.6 16.1 12.5 128. 0.6 90.7 251. 524.
# 7 H11 1 1.7 0.8 0.5 25 16.7 15.2 140. 0.6 90.3 264. 535.
# 8 H11 2 2.1 1.1 0.5 26.5 14.3 13.5 114. 0.6 89.3 288. 397
# 9 H11 3 2.5 1.4 0.6 27.5 15.2 19.4 168. 0.6 89.6 315. 532.
# 10 H12 1 2.5 1.5 0.6 28.4 15 18.2 153. 0.6 89.2 291. 525.
# # ... with 29 more rows
remove_rows_zero(data_naz)
# Warning: Row(s) 2, 6, 9 with 0s deleted.
# # A tibble: 36 x 17
# GEN REP PH EH EP EL ED CL CD CW KW NR NKR
# <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
# 1 H1 1 2.1 1 0.5 15.7 49.9 30.5 16.6 28.6 164. 15.6 31.2
# 2 H1 3 2.3 1.2 0.5 15.1 52.6 31.7 16.2 29.6 176 15.6 29.2
# 3 H10 1 1.8 0.9 0.5 13.9 44.1 26.2 15 12.9 116. 14.8 33
# 4 H10 2 2.1 1 0.5 13.6 43.9 23.5 14.4 11.5 118. 16 32.4
# 5 H11 1 1.7 0.8 0.5 15.5 45.2 25 16.7 15.2 140. 15.6 36
# 6 H11 2 2.1 1.1 0.5 12.2 46.9 26.5 14.3 13.5 114. 16.8 26.2
# 7 H12 1 2.5 1.5 0.6 14.4 49.2 28.4 15 18.2 153. 16.4 32
# 8 H12 2 2.8 1.6 0.6 13.8 46.5 23.8 14.6 16.3 153. 17.6 31.4
# 9 H12 3 2 0.8 0.4 13.7 47.5 25.3 14.3 18.9 139. 14.8 25.4
# 10 H13 1 2.5 1.1 0.4 16.1 51.7 28.2 16.6 23.9 199. 18 30.8
# # ... with 26 more rows, and 4 more variables: CDED <dbl>, PERK <dbl>,
# # TKW <dbl>, NKE <dbl>
select_cols_zero(data_naz)
# Warning: Column(s) with 0s: EL, ED, NR, NKR
# # A tibble: 39 x 4
# EL ED NR NKR
# <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
# 1 15.7 49.9 15.6 31.2
# 2 0 0 0 0
# 3 15.1 52.6 15.6 29.2
# 4 13.9 44.1 14.8 33
# 5 13.6 43.9 16 32.4
# 6 0 0 0 0
# 7 15.5 45.2 15.6 36
# 8 12.2 46.9 16.8 26.2
# 9 0 0 0 0
# 10 14.4 49.2 16.4 32
# # ... with 29 more rows
select_rows_zero(data_naz)
# Warning: Rows(s) with 0s: 1, 2, 3
# # A tibble: 3 x 17
# GEN REP PH EH EP EL ED CL CD CW KW NR NKR
# <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
# 1 H1 2 2.2 1.1 0.5 0 0 30.5 14.7 22.3 130. 0 0
# 2 H10 3 2.3 1.1 0.5 0 0 24.6 16.1 12.5 128. 0 0
# 3 H11 3 2.5 1.4 0.6 0 0 27.5 15.2 19.4 168. 0 0
# # ... with 4 more variables: CDED <dbl>, PERK <dbl>, TKW <dbl>, NKE <dbl>
replace_zero(data_naz)
# # A tibble: 39 x 17
# GEN REP PH EH EP EL ED CL CD CW KW NR NKR
# <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
# 1 H1 1 2.1 1 0.5 15.7 49.9 30.5 16.6 28.6 164. 15.6 31.2
# 2 H1 2 2.2 1.1 0.5 NA NA 30.5 14.7 22.3 130. NA NA
# 3 H1 3 2.3 1.2 0.5 15.1 52.6 31.7 16.2 29.6 176 15.6 29.2
# 4 H10 1 1.8 0.9 0.5 13.9 44.1 26.2 15 12.9 116. 14.8 33
# 5 H10 2 2.1 1 0.5 13.6 43.9 23.5 14.4 11.5 118. 16 32.4
# 6 H10 3 2.3 1.1 0.5 NA NA 24.6 16.1 12.5 128. NA NA
# 7 H11 1 1.7 0.8 0.5 15.5 45.2 25 16.7 15.2 140. 15.6 36
# 8 H11 2 2.1 1.1 0.5 12.2 46.9 26.5 14.3 13.5 114. 16.8 26.2
# 9 H11 3 2.5 1.4 0.6 NA NA 27.5 15.2 19.4 168. NA NA
# 10 H12 1 2.5 1.5 0.6 14.4 49.2 28.4 15 18.2 153. 16.4 32
# # ... with 29 more rows, and 4 more variables: CDED <dbl>, PERK <dbl>,
# # TKW <dbl>, NKE <dbl>
- New argument
positioninplot.gamem()andplot.mtsi()to control the position adjustment of the bar plot.
rcbd <- gamem(data_g,
gen = GEN,
rep = REP,
resp = c(PH, ED, EL, CL, NR))
# Evaluating trait PH |========= | 20% 00:00:00
Evaluating trait ED |================== | 40% 00:00:00
Evaluating trait EL |========================== | 60% 00:00:00
Evaluating trait CL |=================================== | 80% 00:00:00
Evaluating trait NR |============================================| 100% 00:00:00
# Method: REML/BLUP
# Random effects: GEN
# Fixed effects: REP
# Denominador DF: Satterthwaite's method
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# P-values for Likelihood Ratio Test of the analyzed traits
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# model PH ED EL CL NR
# Complete NA NA NA NA NA
# Genotype 0.051 2.73e-05 0.786 2.25e-06 0.0056
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Variables with nonsignificant Genotype effect
# PH EL
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
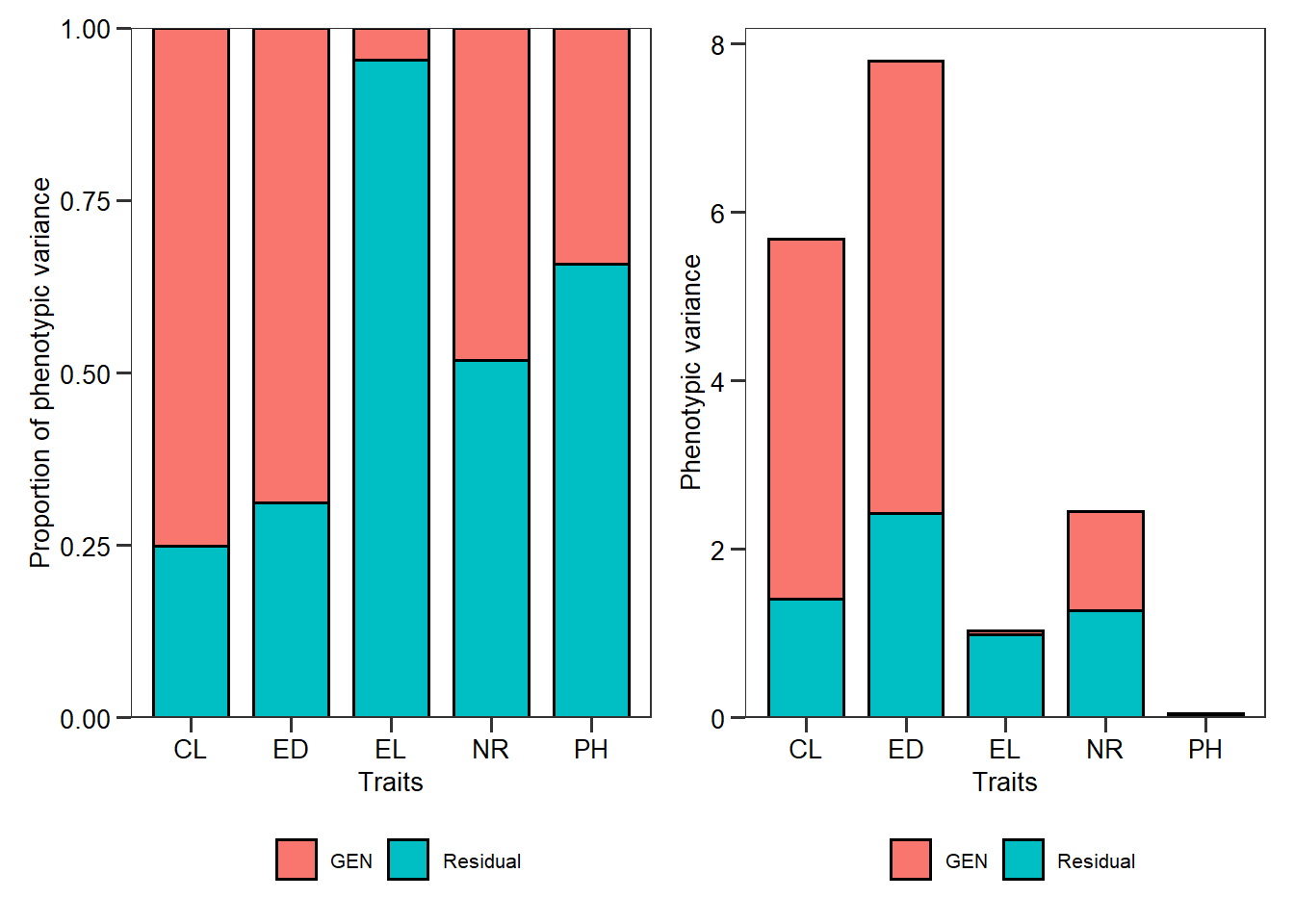
p1 <- plot(rcbd, type = "vcomp")
p2 <- plot(rcbd, type = "vcomp", position = "stack")
arrange_ggplot(p1, p2)
- New argument
col.byincorr_plot()to map the color of the points by a categorical variable.
corr_plot(iris, col.by = Species)